dev-master
9999999-dev https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- php ^7.0
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- oscarotero/fol ^0.3
- oscarotero/middleland ^1.0
- psr/http-server-middleware ^1.0
- middlewares/base-path ^1.0
- middlewares/method-override ^1.0
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^1.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^1.0
- middlewares/cache ^1.0
- middlewares/negotiation ^1.0
- middlewares/filesystem ^1.0
- middlewares/request-handler ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.7.1
3.7.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.3
- oscarotero/middleland ^1.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- psr/http-server-middleware ^1.0
- middlewares/base-path ^1.0
- middlewares/method-override ^1.0
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^1.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^1.0
- middlewares/cache ^1.0
- middlewares/negotiation ^1.0
- middlewares/filesystem ^1.0
- middlewares/request-handler ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.7.0
3.7.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.3
- oscarotero/middleland ^1.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- psr/http-server-middleware ^1.0
- middlewares/base-path ^1.0
- middlewares/method-override ^1.0
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^1.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^1.0
- middlewares/cache ^1.0
- middlewares/negotiation ^1.0
- middlewares/filesystem ^1.0
- middlewares/request-handler ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.6.3
3.6.3.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.3
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.4
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache *
- middlewares/base-path *
- middlewares/trailing-slash *
- middlewares/negotiation *
- middlewares/method-override *
- middlewares/filesystem *
- middlewares/aura-router *
- http-interop/http-server-middleware ^1.0
- middlewares/request-handler *
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.6.2
3.6.2.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.3
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.4
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache *
- middlewares/base-path *
- middlewares/trailing-slash *
- middlewares/negotiation *
- middlewares/method-override *
- middlewares/filesystem *
- middlewares/aura-router *
- http-interop/http-server-middleware ^1.0
- middlewares/request-handler *
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.6.1
3.6.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.3
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.4
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache *
- middlewares/base-path *
- middlewares/trailing-slash *
- middlewares/negotiation *
- middlewares/method-override *
- middlewares/filesystem *
- middlewares/aura-router *
- http-interop/http-server-middleware ^1.0
- middlewares/request-handler *
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.6.0
3.6.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.3
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.4
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache *
- middlewares/base-path *
- middlewares/trailing-slash *
- middlewares/negotiation *
- middlewares/method-override *
- middlewares/filesystem *
- middlewares/aura-router *
- http-interop/http-server-middleware ^1.0
- middlewares/request-handler *
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.5.1
3.5.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.3
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.4
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache *
- middlewares/base-path *
- middlewares/trailing-slash *
- middlewares/negotiation *
- middlewares/method-override *
- middlewares/filesystem *
- middlewares/aura-router *
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.5
- middlewares/request-handler *
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.5.0
3.5.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.3
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.4
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache *
- middlewares/base-path *
- middlewares/trailing-slash *
- middlewares/negotiation *
- middlewares/method-override *
- middlewares/filesystem *
- middlewares/aura-router *
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.5
- middlewares/request-handler *
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.4.1
3.4.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.2
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.4
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.7
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.4
- middlewares/request-handler ^0.2.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.4.0
3.4.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.2
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.4
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.6
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.5
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.4
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
dev-redesign
dev-redesign https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.2
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.4
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.6
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.5
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.4
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.3.0
3.3.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.2
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.4
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.6
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.5
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.4
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.2.1
3.2.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.2
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.4
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.6
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.5
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.4
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.2.0
3.2.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.2
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.4
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.5
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.5
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.4
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.1.0
3.1.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.1
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.2
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.5
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.4
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.4
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.0.4
3.0.4.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.1
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.2
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.5
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.4
- middlewares/http-authentication ^0.3
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.4
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.0.3
3.0.3.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.1
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.2
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.4
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.4
- middlewares/http-authentication ^0.3
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.4
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.0.2
3.0.2.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.1
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.2
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.4
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.3
- middlewares/http-authentication ^0.3
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.4
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.0.1
3.0.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.1
- oscarotero/middleland ~0.2
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.4
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.3
- middlewares/http-authentication ^0.3
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.4
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v3.0.0
3.0.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php ^7.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- oscarotero/fol ^0.1
- oscarotero/middleland ^0.2
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.4
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.3
- middlewares/http-authentication ^0.3
- http-interop/http-middleware ^0.4
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v2.5.0
2.5.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/utils ~0.8
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.4.0
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3.0
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3.0
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3.0
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3.0
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.3.0
- middlewares/http-authentication ^0.3.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v2.4.1
2.4.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/utils ~0.8
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.4.0
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3.0
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3.0
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3.0
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3.0
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.3.0
- middlewares/http-authentication ^0.3.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v2.4.0
2.4.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/utils ~0.8
- middlewares/cache ^0.3.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.4.0
- middlewares/base-path ^0.3.0
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.3.0
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.3.0
- middlewares/method-override ^0.3.0
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.3.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.3.0
- middlewares/http-authentication ^0.3.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v2.3.0
2.3.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- middlewares/utils ~0.5
- middlewares/cache ^0.2.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.3.0
- middlewares/base-path ^0.2.0
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.2.0
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.2.0
- middlewares/method-override ^0.2.0
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.2.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.2.0
- middlewares/http-authentication ^0.2.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v2.2.4
2.2.4.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- mindplay/middleman ^2.0
- middlewares/cache ^0.1.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.2.0
- middlewares/base-path ^0.1.1
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.1.1
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.1.0
- middlewares/method-override ^0.1.1
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.1.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.1.1
- middlewares/http-authentication ^0.1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v2.2.3
2.2.3.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- mindplay/middleman ^2.0
- middlewares/cache ^0.1.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.1.0
- middlewares/base-path ^0.1.1
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.1.1
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.1.0
- middlewares/method-override ^0.1.1
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.1.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.1.1
- middlewares/http-authentication ^0.1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v2.2.2
2.2.2.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- mindplay/middleman ^2.0
- middlewares/cache ^0.1.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.1.0
- middlewares/base-path ^0.1.1
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.1.1
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.1.0
- middlewares/method-override ^0.1.1
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.1.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.1.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v2.2.1
2.2.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- mindplay/middleman ^2.0
- middlewares/cache ^0.1.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.1.0
- middlewares/base-path ^0.1.1
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.1.1
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.1.0
- middlewares/method-override ^0.1.1
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.1.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.1.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v2.2.0
2.2.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- mindplay/middleman ^2.0
- middlewares/cache ^0.1.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.1.0
- middlewares/base-path ^0.1.1
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.1.1
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.1.0
- middlewares/method-override ^0.1.1
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.1.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.1.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v2.1.0
2.1.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- mindplay/middleman ^2.0
- middlewares/cache ^0.1.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.1.0
- middlewares/base-path ^0.1.1
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.1.1
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.1.0
- middlewares/method-override ^0.1.1
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.1.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.1.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v2.0.0
2.0.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- league/plates ^3.1
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
- mindplay/middleman ^2.0
- middlewares/cache ^0.1.0
- middlewares/error-handler ^0.1.0
- middlewares/base-path ^0.1.1
- middlewares/trailing-slash ^0.1.1
- middlewares/negotiation ^0.1.0
- middlewares/method-override ^0.1.1
- middlewares/filesystem ^0.1.0
- middlewares/aura-router ^0.1.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
1.x-dev
1.9999999.9999999.9999999-dev https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.14.3
1.14.3.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.14.2
1.14.2.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.14.1
1.14.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.14.0
1.14.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.13.2
1.13.2.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.13.1
1.13.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.4
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^2.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.13.0
1.13.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.3
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.12.2
1.12.2.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.3
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.12.1
1.12.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.3
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.12.0
1.12.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.3
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.11.2
1.11.2.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.3
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.11.1
1.11.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.3
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
1.11.0
1.11.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.3
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
- imagecow/imagecow ^2.1
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.10.5
1.10.5.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.3
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.10.4
1.10.4.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.3
- gettext/gettext ^4.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.10.3
1.10.3.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.16.1
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.3
- gettext/gettext ^3.6
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.10.2
1.10.2.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.15
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.3
- gettext/gettext ^3.6
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.10.1
1.10.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.15
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0.3
- gettext/gettext ^3.6
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.10.0
1.10.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.15
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^3.6
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
1.9.2
1.9.2.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.15
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^3.6
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.9.1
1.9.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.15
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^3.6
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.9.0
1.9.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.15
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^3.6
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.8.1
1.8.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.15
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext ^3.6
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
1.8.0
1.8.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.15
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^5.0
- gettext/gettext dev-master
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.7.2
1.7.2.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.15
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.7.1
1.7.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.15
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.7.0
1.7.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.15
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
- oscarotero/inline-svg ^1.0
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.6.0
1.6.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.14
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.5.2
1.5.2.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.14
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.5.1
1.5.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.14
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.5.0
1.5.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.14
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
psr-7 crud cms admin
v1.4.0
1.4.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.14
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
The Development Requires
by Oscar Otero
cms
v1.3.0
1.3.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.14
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
by Oscar Otero
cms
v1.2.0
1.2.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.14
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
by Oscar Otero
cms
v1.1.0
1.1.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.10
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
by Oscar Otero
cms
v1.0.2
1.0.2.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.10
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
by Oscar Otero
cms
v1.0.1
1.0.1.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.10
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
by Oscar Otero
cms
v1.0.0
1.0.0.0 https://github.com/fol-project/folUniversal CMS
MIT
The Requires
- php >=5.5.0
- zendframework/zend-diactoros ^1.3
- relay/relay ^1.1
- league/plates ^3.1
- aura/router ^3.0
- oscarotero/psr7-middlewares ^3.10
- willdurand/negotiation ^2.0
- fol/core ^11.1
- form-manager/form-manager ^4.7
by Oscar Otero
cms
 Wallogit.com
Wallogit.com

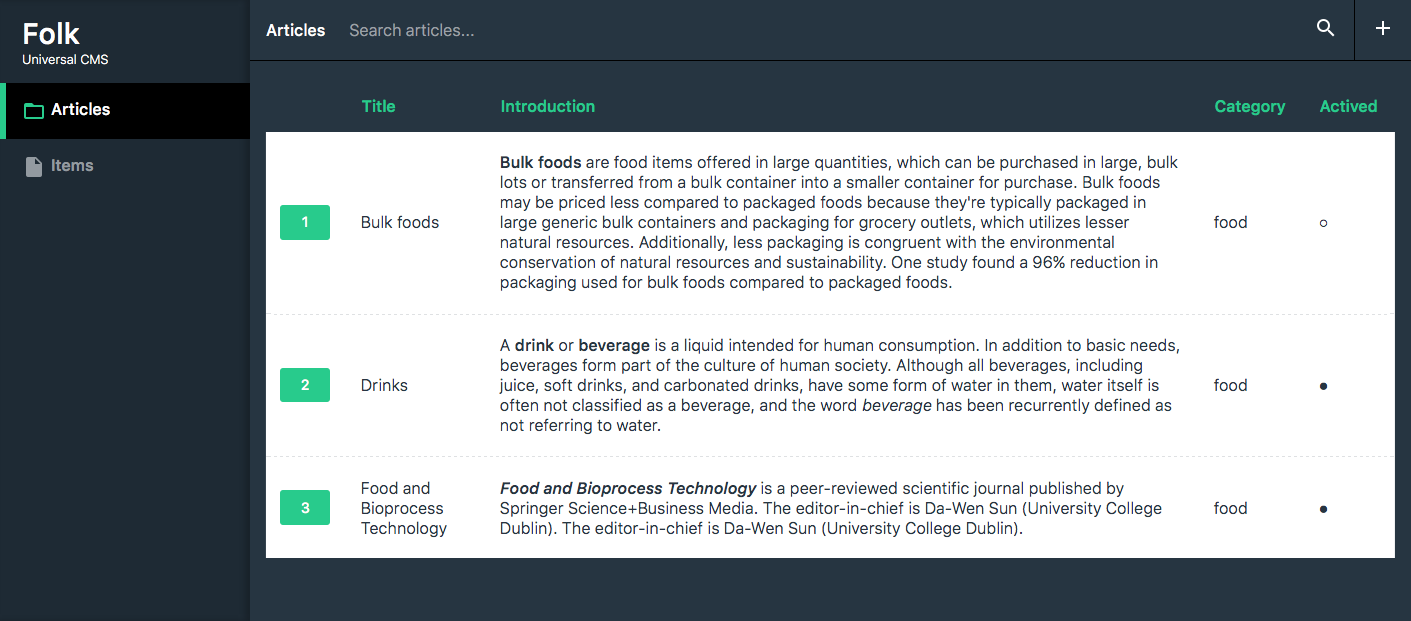
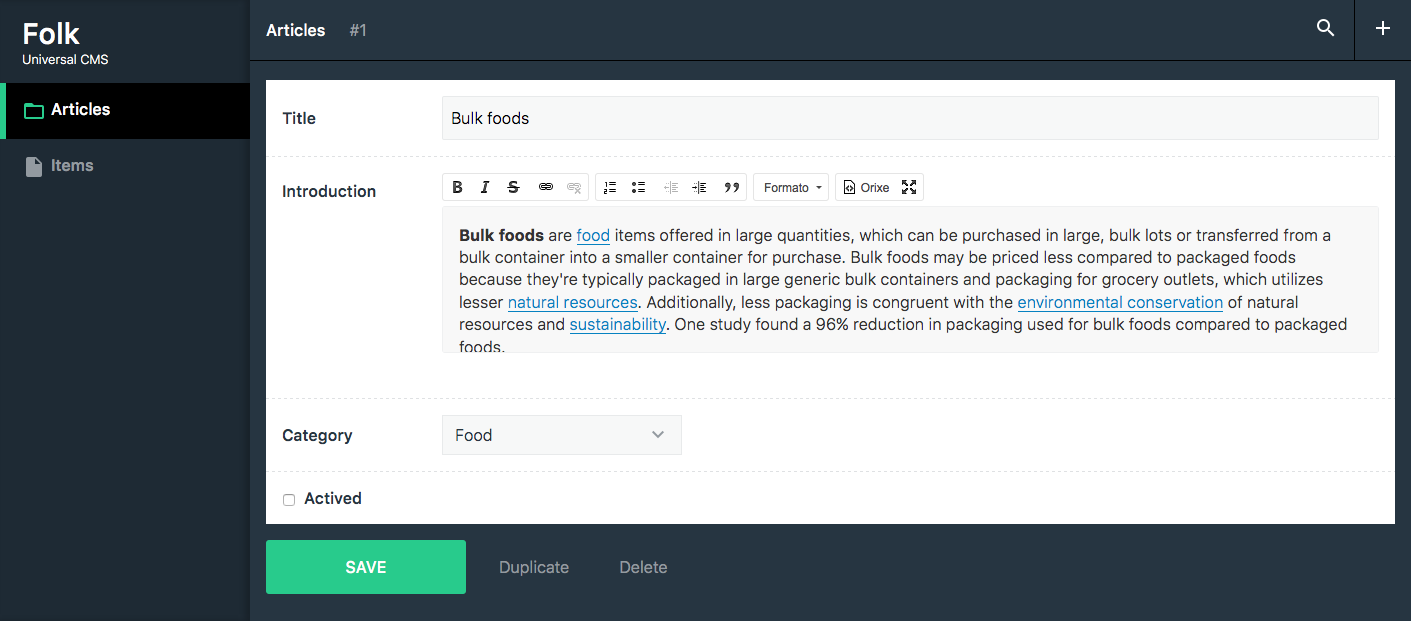 , (*5)
, (*5)